Traffic Streams
Traffic streams allow doing various forwarding verification and QoS tests using BNG Blaster.
Traffic streams are divided into bounded and RAW streams. The first one is bound to an access configuration and derives addresses dynamically from the sessions.
RAW streams are supported from network interfaces only.
Configuration
Following a simple PPPoE example with streams.
{
"interfaces": {
"network": {
"interface": "eth2",
"address": "10.0.0.1/24",
"gateway": "10.0.0.2",
"address-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331::1/64",
"gateway-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331::2"
},
"access": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"outer-vlan-min": 1001,
"outer-vlan-max": 2000,
"inner-vlan-min": 7,
"inner-vlan-max": 7,
"type": "pppoe",
"stream-group-id": 1
},
{
"interface": "eth1",
"outer-vlan-min": 2001,
"outer-vlan-max": 4000,
"inner-vlan": 7,
"type": "pppoe",
"stream-group-id": 2
}
]
},
"streams": [
{
"name": "BestEffort",
"stream-group-id": 1,
"type": "ipv4",
"direction": "both",
"pps": 1000
},
{
"name": "Voice",
"stream-group-id": 1,
"type": "ipv4",
"direction": "downstream",
"priority": 128,
"vlan-priority": 2,
"network-ipv4-address": "10.0.0.10",
"pps": 100
},
{
"name": "BestEffort",
"stream-group-id": 2,
"type": "ipv4",
"direction": "both",
"pps": 1
}
]
}
{ "streams": {} }
Attribute |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
name |
Mandatory stream name |
|
stream-group-id |
Stream group identifier |
0 (raw) |
type |
Mandatory stream type (ipv4, ipv6 or ipv6pd) |
|
direction |
Mandatory stream direction (upstream, downstream or both) |
both |
source-port |
Overwrite the default source port |
65056 |
destination-port |
Overwrite the default destination port |
65056 |
ipv4-df |
Set IPv4 DF bit |
true |
priority |
IPv4 TOS / IPv6 TC |
0 |
vlan-priority |
VLAN priority |
0 |
length |
Layer 3 (IP header + payload) traffic length (76 - 9000) |
128 |
pps |
Stream traffic rate in packets per second |
1 |
bps |
Stream traffic rate in bits per second (layer 3) |
|
a10nsp-interface |
Select the corresponding A10NSP interface for this stream |
|
network-interface |
Select the corresponding network interface for this stream |
|
network-ipv4-address |
Overwrite network interface IPv4 address |
|
network-ipv6-address |
Overwrite network interface IPv6 address |
|
destination-ipv4-address |
Overwrite the IPv4 destination address |
|
destination-ipv6-address |
Overwrite the IPv6 destination address |
|
access-ipv4-source-address |
Overwrite the access IPv4 source address (client) |
|
access-ipv6-source-address |
Overwrite the access IPv6 source address (client) |
|
max-packets |
Send a burst of N packets and stop |
0 (infinity) |
start-delay |
Wait N seconds after the session is established before starting |
0 |
tx-label1 |
MPLS send (TX) label (outer label) |
|
tx-label1-exp |
EXP bits of the first label (outer label) |
0 |
tx-label1-ttl |
TTL of the first label (outer label) |
255 |
tx-label2 |
MPLS send (TX) label (inner label) |
|
tx-label2-exp |
EXP bits of the second label (inner label) |
0 |
tx-label2-ttl |
TTL of the second label (inner label) |
255 |
rx-label1 |
Expected receive MPLS label (outer label) |
|
rx-label2 |
Expected receive MPLS label (inner label) |
|
ldp-ipv4-lookup-address |
Dynamically resolve outer label |
For L2TP downstream traffic, the IPv4 TOS is applied to the outer IPv4 and inner IPv4 header.
The pps option supports also float numbers like 0.1, or 2.5 PPS and has
priority over bps where the second is only a helper to calculate the pps
based on given bps and length. The resulting rate in bps is the
layer 3 rate because length is also the layer 3 length (IP header + payload).
It is also supported to put the capital letters K (Kilo), M (Mega)
or G (Giga) in front of bps for better readability.
For example "Gbps": 1 which is equal to "bps": 1000000000.
The options access-ipv4-source-address and access-ipv6-source-address
can be used to test the BNG RPF functionality with traffic sent from source addresses
different than those assigned to the client.
Stream Configuration File
The command line argument -T <filename> allows the include
of streams defined in a separate file. The format is equal to
streams defined in the actual configuration file. Such stream
configuration files could be generated by scripts and
easily merged with the base configuration.
{
"streams": []
}
Stream Commands
The session-streams command returns detailed stream statistics per session.
$ sudo bngblaster-cli run.sock session-streams session-id 1
{
"status": "ok",
"code": 200,
"session-streams": {
"session-id": 1,
"rx-packets": 59670,
"tx-packets": 54610,
"rx-accounting-packets": 59655,
"tx-accounting-packets": 54594,
"rx-pps": 1100,
"tx-pps": 1000,
"rx-bps-l2": 9028800,
"tx-bps-l2": 8240000,
"rx-mbps-l2": 9.0288,
"tx-mbps-l2": 8.24,
"streams": [
{
"name": "BestEffort",
"direction": "upstream",
"flow-id": 1,
"rx-first-seq": 362,
"rx-last-seq": 54593,
"rx-tos-tc": 0,
"rx-outer-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-inner-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-len": 1014,
"tx-len": 1030,
"rx-packets": 54232,
"tx-packets": 54594,
"rx-loss": 0,
"rx-delay-us-min": 37,
"rx-delay-us-max": 98595,
"rx-pps": 1000,
"tx-pps": 1000,
"tx-bps-l2": 8240000,
"rx-bps-l2": 8112000,
"rx-bps-l3": 8000000,
"tx-mbps-l2": 8.24,
"rx-mbps-l2": 8.112,
"rx-mbps-l3": 8.0
},
{
"name": "BestEffort",
"direction": "downstream",
"flow-id": 2,
"rx-first-seq": 362,
"rx-last-seq": 54593,
"rx-tos-tc": 0,
"rx-outer-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-inner-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-len": 1026,
"tx-len": 1014,
"rx-packets": 54232,
"tx-packets": 54594,
"rx-loss": 0,
"rx-delay-us-min": 43,
"rx-delay-us-max": 98903,
"rx-pps": 1000,
"tx-pps": 1000,
"tx-bps-l2": 8112000,
"rx-bps-l2": 8208000,
"rx-bps-l3": 8000000,
"tx-mbps-l2": 8.112,
"rx-mbps-l2": 8.208,
"rx-mbps-l3": 8.0
},
{
"name": "Voice",
"direction": "downstream",
"flow-id": 3,
"rx-first-seq": 37,
"rx-last-seq": 5458,
"rx-tos-tc": 128,
"rx-outer-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-inner-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-len": 1026,
"tx-len": 1014,
"rx-packets": 5422,
"tx-packets": 5458,
"rx-loss": 0,
"rx-delay-us-min": 41,
"rx-delay-us-max": 96548,
"rx-pps": 100,
"tx-pps": 100,
"tx-bps-l2": 811200,
"rx-bps-l2": 820800,
"rx-bps-l3": 800000,
"tx-mbps-l2": 0.8112,
"rx-mbps-l2": 0.8208,
"rx-mbps-l3": 0.8
}
]
}
}
The rx-outer-vlan-pbit might be wrong depending on the network interface driver and
optional VLAN offloading.
The measured rx-delay-us-min/max shows the minimum and maximum calculated delay
in microseconds. The delay is calculated by subtracting the send and receive timestamp.
The send timestamp is stored in the BBL header (see section Traffic). This calculated
result depends also on the actual test environment, configured rx-interval and host IO
delay.
Traffic streams will start as soon as the session is established using the rate as configured
starting with sequence number 1 for each flow. The attribute rx-first-seq stores the first
sequence number received. Assuming the first sequence number received for a given flow is 1000
combined with a rate of 1000 PPS would mean that it took around 1 second until forwarding is
working. After the first packet is received for a given flow, for every further packet it checks
if there is a gap between the last and new sequence number which is then reported as a loss.
The rx/tx-accounting-packets are all packets that should be counted in the session volume
accounting of the BNG, meaning session RX/TX packets excluding control traffic.
Each flow can be queried separately using jsonpath expression with name and direction or flow-id.
$ sudo bngblaster-cli run.sock session-streams session-id 1 | jq '."session-streams".streams[] | select(.name == "BE" and .direction == "downstream" )'
{
"name": "BE",
"direction": "downstream",
"flow-id": 2,
"rx-first-seq": 33,
"rx-last-seq": 27040,
"rx-tos-tc": 213,
"rx-outer-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-inner-vlan-pbit": 0,
"rx-len": 126,
"tx-len": 114,
"rx-packets": 27008,
"tx-packets": 27040,
"rx-loss": 0,
"rx-delay-us-min": 50,
"rx-delay-us-max": 10561,
"rx-pps": 99,
"tx-pps": 99,
"tx-bps-l2": 90288,
"rx-bps-l2": 99792,
"rx-bps-l3": 79200,
"tx-mbps-l2": 0.090288,
"rx-mbps-l2": 0.099792,
"rx-mbps-l3": 0.0792
}
RAW Streams
Streams with default stream-group-id set to zero are considered raw streams not
bound to any session which is supported downstream only. For those streams, the
destination address must be explicitly set.
RAW streams can be used for traffic between two or network interfaces but also to send traffic from network to access interfaces.
{
"streams": [
{
"name": "RAW",
"type": "ipv4",
"direction": "downstream",
"priority": 128,
"network-ipv4-address": "10.0.0.20",
"destination-ipv4-address": "1.1.1.1",
"length": 256,
"pps": 1
}
]
}
If destination-ipv4-address is set to a multicast IP address (224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255),
the BNG Blaster will set the destination MAC address to the corresponding
multicast MAC address automatically. For unicast traffic the network gateway MAC address is used.
Start/Stop Session Stream Traffic
Session stream traffic can be started/stopped dynamically
using the commands stream-traffic-enabled and stream-traffic-disabled.
$ sudo bngblaster-cli run.sock stream-traffic-disabled session-id 1
Those commands start/stop the traffic for all sessions if invoked without session identifier.
$ sudo bngblaster-cli run.sock stream-traffic-disabled
Alternatively, all the session and stream traffic (including RAW streams)
can be started or stopped globally using the traffic-start and
traffic-stop commands.
BNG Blaster Traffic
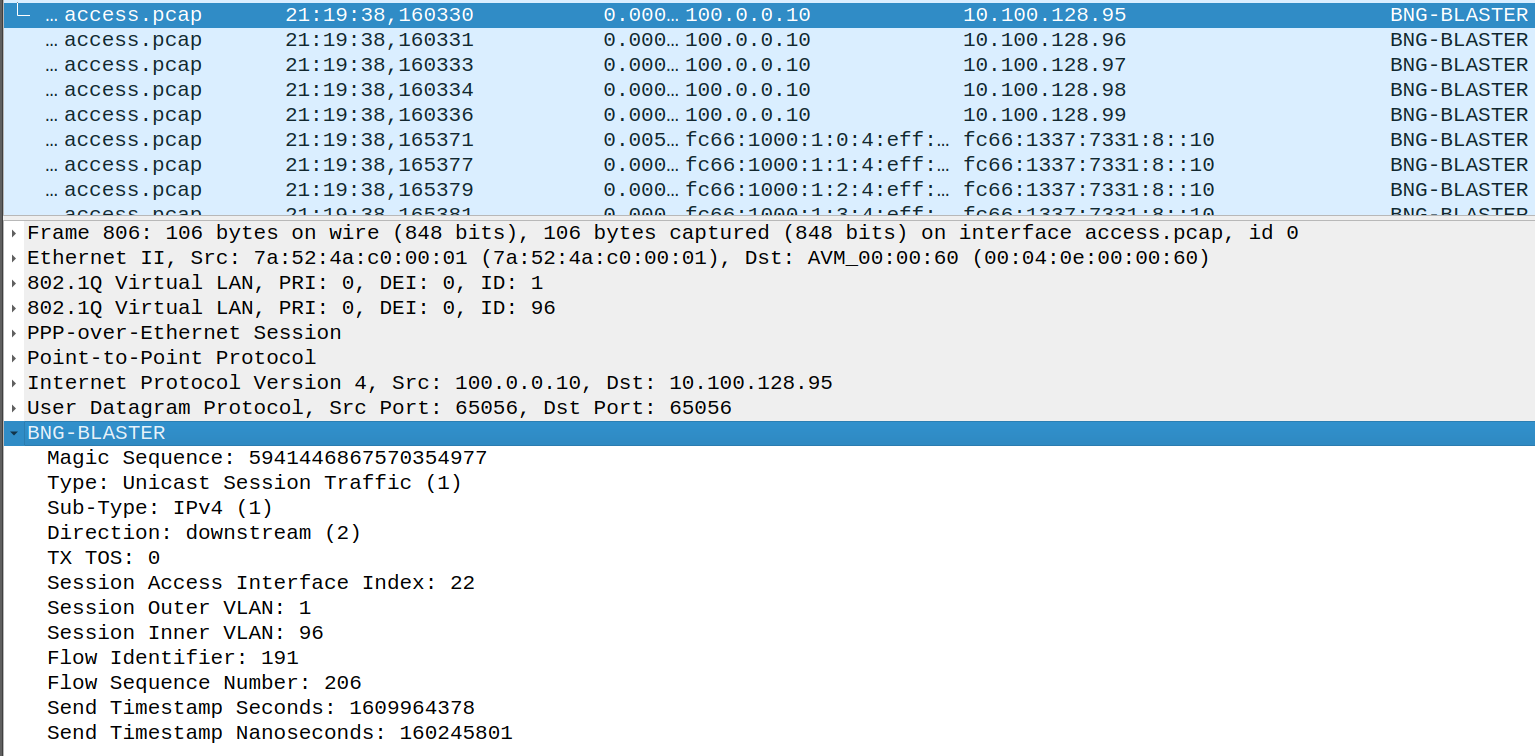
Blaster Header and Fast Decode Signature
The 48 Byte fixed size BNG Blaster Header is added to all data packets for traffic validation and fast decoding. The header is expected on the last 48 bytes of the packet.
The type is set to 1 for all unicast session traffic and 2 for IPv4 multicast traffic.
Unicast Session Traffic
The 64-bit session key is used for all traffic from access (upstream) and to access (downstream) interfaces to identify the corresponding session which has sent or should receive the packet.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| BNG Blaster Magic Sequence |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Type | Sub-Type | Direction | TX TOS |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Session Identifier |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Session Access Interface Index |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Session Outer VLAN | Session Inner VLAN |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Flow Identifier |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Flow Sequence Number |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Nanosecond Send Timestamp |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
Multicast Traffic
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| BNG Blaster Magic Sequence |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Type | Sub-Type | Direction | TX TOS |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Reserved |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Source |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Group |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Flow Identifier |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Flow Sequence Number |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Nanosecond Send Timestamp |
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
Note
All attributes except IP addresses in the Blaster Header are stored in host byte order for faster processing (LE or BE depending on the test system).
BNG Blaster Magic Sequence
The 64-bit magic sequence is the word RtBrick! decoded as ASCII:
0x5274427269636b21
Storing the magic number on a fixed offset allows fast identification of blaster traffic.
Flow Identifier
The 64-bit flow identifier is a globally unique number that identifies the flow.
Flow Sequence Number
The 64-bit flow sequence number is a sequential number starting with 1 and incremented per packet primary used to identify packet loss.
This number 0 means that sequencing is disabled.
Nanosecond Send Timestamps
The 64-bit nanoseconds send timestamp is used for optional latency and jitter calculations.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Seconds |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Nano Seconds |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
The timestamp 0 means that timestamps are disabled.